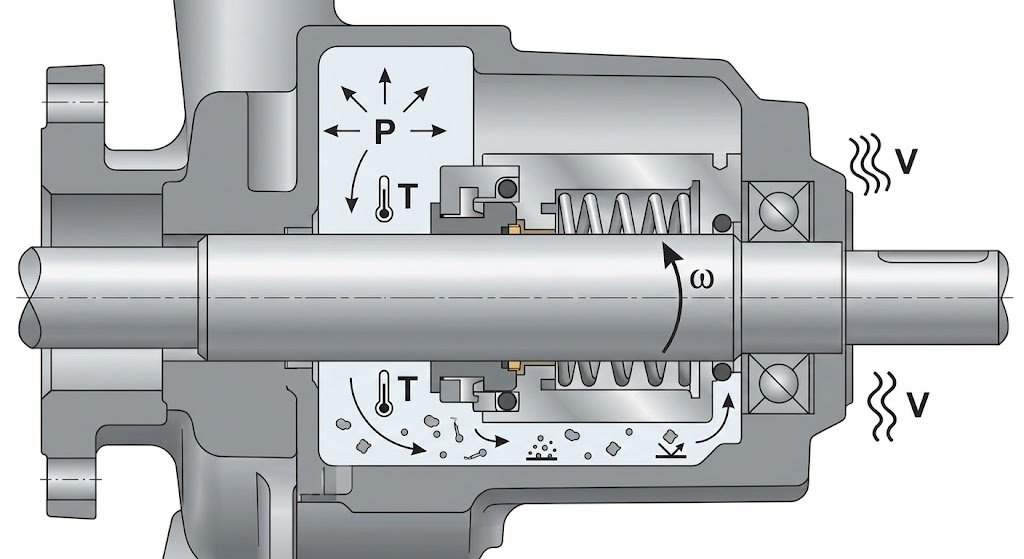
Mechanical seal service life is one of the most common concerns for pump operators and maintenance engineers. When a seal fails earlier than expected, it is often described as a “quality issue.” In reality, seal lifespan is determined by a combination of technical and operational factors, not by seal design alone.
Understanding what truly determines mechanical seal service life helps users reduce unplanned downtime, lower maintenance costs, and make better seal selection decisions.
1. Operating Conditions Are the Primary Factor
The most important determinant of mechanical seal service life is operating conditions. Even a high-quality seal will fail prematurely if it operates outside its intended range.
Key operating factors include:
-
Presión
-
Temperatura
-
Pump speed (RPM)
-
Process fluid characteristics
-
Duty cycle and stability
Mechanical seals are designed for specific operating windows. Exceeding those limits significantly shortens service life.
2. Seal Face Materials and Their Compatibility
Seal faces are the core working surfaces of a mechanical seal. Their material selection directly affects wear rate and reliability.
Common seal face materials include:
-
Carbon
-
Silicon carbide (SiC)
-
Tungsten carbide (TC)
Seal life depends on whether these materials are properly matched to:
-
Operating pressure
-
Temperatura
-
Lubrication quality
-
Presence of solids or abrasives
Incorrect material pairing often results in accelerated wear rather than immediate failure.
3. Elastomers and Secondary Sealing Elements
Elastomers such as O-rings and bellows are often overlooked, but they play a critical role in seal performance.
Factors affecting elastomer life include:
-
Temperature resistance
-
Chemical compatibility
-
Compression set
-
Aging and hardening
Elastomer degradation can lead to leakage even when seal faces remain in good condition.
4. Installation Quality and Alignment
Installation errors are one of the most common reasons for reduced seal life.
Typical installation-related issues include:
-
Shaft misalignment
-
Excessive runout
-
Uneven gland tightening
-
Contamination of seal faces during installation
Even cartridge mechanical seals, which simplify installation, still require proper procedures to achieve expected service life.
5. Shaft Condition and Equipment Health
Mechanical seals do not operate independently of the pump. Shaft condition and overall equipment health strongly influence seal lifespan.
Critical factors include:
-
Shaft surface finish
-
Radial and axial movement
-
Bearing condition
-
Vibration levels
Excessive vibration or shaft movement accelerates seal face wear and shortens service life.
6. Process Fluid Quality and Lubrication
The process fluid itself acts as a lubricant for seal faces. Poor lubrication conditions increase friction and heat generation.
Seal life is reduced when:
-
The fluid has low lubricity
-
Solids or crystals are present
-
The seal runs dry during startup
-
Flush systems are inadequate or blocked
Stable lubrication is essential for long-term seal performance.
7. Thermal Cycling and Start-Stop Frequency
Frequent start-stop cycles expose seals to repeated thermal expansion and contraction. Over time, this leads to material fatigue and loss of sealing integrity.
Applications with frequent cycling require seals designed to tolerate thermal shock and dynamic movement.
8. Seal Design and Application Matching
Seal design must match the application. Using a standard seal in a demanding application often results in shortened service life.
Examples include:
-
Using single seals in high-pressure environments
-
Applying general-purpose seals in aggressive chemical services
-
Ignoring the need for balanced or cartridge designs
Proper application matching is often more important than seal brand or price.
Conclusión
Mechanical seal service life in industrial pumps is determined by a combination of operating conditions, material selection, installation quality, and equipment health. Seal failure is rarely caused by a single factor.
By understanding these determinants, pump users can move from reactive maintenance to proactive seal management—extending seal life, improving reliability, and reducing total operating costs.
👉https://sakowit.com/mechanical-seal-installation-guide-best-practices-to-prevent-early-failure/




